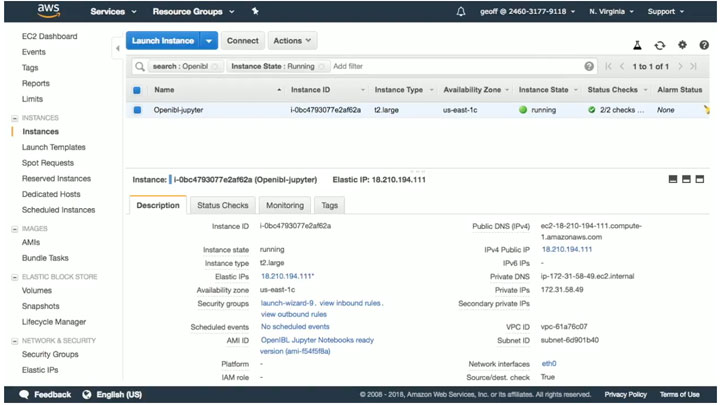
IBL Education is launching today a Jupyter Notebook – ready Open edX distribution. Open IBL Jupyter Notebook is built on the Ginkgo.2 version of Open edX. This release is free and is ready to go from the AWS (Amazon Web Services) AMI community.
In June, the IBL engineering team launched Open IBL, an easy-to-handle, production-ready distribution based on Open edX’s Ginkgo.2, which was equipped with a command-line builder. These two screencast videos explained the installation and configuration process. (Video 1, Video 2)
This week, in parallel with the Jupyter Conference in New York (Aug 22-24), and also as a contribution to the educational community, IBL launches another version of the Open IBL distribution which includes the two recent Jupyter Notebooks-related Xblocks:
1. Jupyter Notebook Viewer XBlock. It allows from any public Jupyter Notebook (e.g., in a public repo on GitHub), pull content into a course learning sequence using only the URL, and optional start and end marks (any string from the first cell to include, and the first cell to exclude). As a result of it, course authors will be able to develop their course content as Jupyter Notebooks, and to build learning sequences reusing that content, without duplication. It also has the added benefit that the development of the material can be hosted on a version-controlled repository. [See IBL’s post about the XBlock, and the code repository—the XBlock is open source under a BSD3 license.]
2. Graded Jupyter Notebook XBlock. It allows to create an assignment using the nbgrader Jupyter extension, then insert a graded sub-section in Open edX that will deliver this assignment (as a download), auto-grade the student’s uploaded solution, and record the student’s score in the gradebook. The XBlock instantiates a Docker container with all the required dependencies, runs nbgrader on the student-uploaded notebook, and displays immediate feedback to the student in the form of a score table. [See IBL’s post, and the code repository—the XBlock is open source under BSD3.]
This Open IBL Jupyter Notebook distribution has been created with the strategic and pedagogical support of Lorena A. Barba group, from The George Washington University.
DEMO of Open IBL Jupyter Notebook
Prof. Barba has been teaching with Jupyter for the last five years. Her first open teaching module using Jupyter was “CFD Python”, released in July 2013. In 2014, Barba developed and taught the first massive open online course (MOOC) at the George Washington University: “Practical Numerical Methods with Python.” The course was written entirely as Jupyter Notebooks, and it was self-hosted on a custom Open edX site (where it amassed more than 8000 users over 3 years).
Jupyter is a set of open-source tools for interactive and exploratory computing. At the center of them is the Jupyter Notebook, a document format for writing narratives that interleave multi-media content with executable code, using any of a set of available languages (of which Python is the most popular).
The two mentioned XBlocks, a brainchild of Prof. Lorena Barba and implemented by her tech partners at IBL Education, were presented at the 2018 Open edX Conference last May 30 in Montreal, Canada. Prof. Lorena Barba, from GW, and Miguel Amigot II, CTO at IBL Education, presented those two software extensions, intended to better integrate Jupyter into the Open edX platform.

 En Español
En Español








![OpenAI Released Apps that Work Inside ChatGPT and an SDK [Video]](https://iblnews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/openaieventday-218x150.jpg)